Laparoscopy
Gynec Laparoscopic Surgeries
1. Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
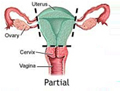 A Hyterectomy can be completed through open, vaginal and laparoscopic approaches. Total laparoscopic Hysterectomies have been found to result in decreased blood loss, shorter hospital and recovery periods and fewer abdominal wall infections than open hysterectomies. We at aaditya fertility center have been doing maximum number of total laparoscopic hysterectomies even for difficult cases like previous caesarean and huge fibroids with specialized instruments like harmonic scalpel and Enseal.
A Hyterectomy can be completed through open, vaginal and laparoscopic approaches. Total laparoscopic Hysterectomies have been found to result in decreased blood loss, shorter hospital and recovery periods and fewer abdominal wall infections than open hysterectomies. We at aaditya fertility center have been doing maximum number of total laparoscopic hysterectomies even for difficult cases like previous caesarean and huge fibroids with specialized instruments like harmonic scalpel and Enseal.
2. Laparoscopy assisted vaignal Hysterectomy
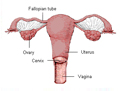 Laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy is a surgical procedure using laparoscope to visulaize the peritoneal cavity and to dissect the uterus from its supports by applying few clamps laparoscopically and few clamps vaginally, and then remove the dissected components via vaginal canal.
Laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy is a surgical procedure using laparoscope to visulaize the peritoneal cavity and to dissect the uterus from its supports by applying few clamps laparoscopically and few clamps vaginally, and then remove the dissected components via vaginal canal.
3. Laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy
 It is the removal of cyst from the ovary done with the intention of conserving the ovaries especially in young patients. It is done for conditions like dermoid cyst, serous or mucinous cyst, Endometriotic cyst and hemorragic cyst. Cyst wall is separated from the ovary with special laparoscopic instruments and it is removed.
It is the removal of cyst from the ovary done with the intention of conserving the ovaries especially in young patients. It is done for conditions like dermoid cyst, serous or mucinous cyst, Endometriotic cyst and hemorragic cyst. Cyst wall is separated from the ovary with special laparoscopic instruments and it is removed.
4. Laparoscopy for Ectopic Pregnancy
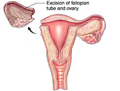
 An Ectopic pregnancy is where the pregnancy takes place outside the uterus usually in the fallopian tubes. Other uncommon sites are ovaries, cervix, and peritoneal cavity. Ectopic pregnancies are not viable and require prompt treatment. The fallopian tube cannot support the growing embryo. After several weeks, the tube may rupture and bleed resulting in a potentially serious situation. Laparoscopy plays an important role in the surgical management of ruptured and unruptured ectopic Pregnancy.
An Ectopic pregnancy is where the pregnancy takes place outside the uterus usually in the fallopian tubes. Other uncommon sites are ovaries, cervix, and peritoneal cavity. Ectopic pregnancies are not viable and require prompt treatment. The fallopian tube cannot support the growing embryo. After several weeks, the tube may rupture and bleed resulting in a potentially serious situation. Laparoscopy plays an important role in the surgical management of ruptured and unruptured ectopic Pregnancy.
5. Laparoscopic sterilisation
 Sterilisation is the permanent method of contraception. Laparoscopic sterilisation is a surgical procedure to prevent pregnancy in which the fallopian tubes are clipped using fallope rings.
Sterilisation is the permanent method of contraception. Laparoscopic sterilisation is a surgical procedure to prevent pregnancy in which the fallopian tubes are clipped using fallope rings.
6. Laparoscopy for Endometriosis
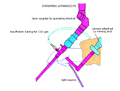 Laparoscopy is the gold standard in the diagnosis and treatment of Endometriosis. Various laparoscopic procedures done for Endometriosis are:
Laparoscopy is the gold standard in the diagnosis and treatment of Endometriosis. Various laparoscopic procedures done for Endometriosis are:
- Chocolate cyst Excision
- Adhesiolysis
- Destruction of endometriotic spots with Cautery
- Presacral neurectomy
- LUNA (Laparoscopic uterosacral nerve ablation)
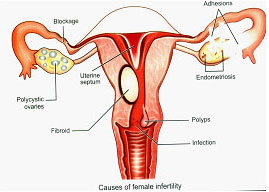
Laparoscopy for Infertility
1. Diagnostic Laparoscopy
Diagnostic laparoscopy forms the cornerstone for the evaluation of an infertile woman. This procedure allows direct visualization of the internal organs where reproduction occurs like uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. It aids in the diagnosis of conditions like Endometriosis, Pelvic tuberculosis which are among the common causes for infertility. Tubal patency can be checked by combining chromotubation.
This procedure is done under general anaesthesia.
2. Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a procedure where the inside of the cervix and uterus is visualized using a camera attached to the TV monitor. It can be either diagnostic or operative Hysteroscopy. Diagnostic Hysteroscopy can be done in the office settings under local anaesthesia. The indications are,
- The study of endocervical mucous lining
- Congenital malformation of the uterus
- Cornual tubal blockage
- Endometrial tuberculosis
- Asherman’s syndrome
3. Diagnostic Hysterolaparoscopy
It is done to evaluate the inside and outside of the uterus simultaneously combining laparoscopy with hysteroscopy. Chromotubation is done with this to check the tubal patency. It is done in the operation room under general anaesthesia.
4. Proximal tubal cannulation
Proximal tubal obstruction is one of the common causes for infertility. Hysteroscopy guided tubal cannulation is a safe and effective procedure for this condition.
5. Hysteroscopic myomectomy
Small submucous fibroid can be removed through hysteroscopy with the help of a specialised instrument called resectoscope.
6. Hysteroscopic Polypectomy
An Endometrial or uterine polyp is a mass in the inner lining of the uterus. Endometrial polyps can be removed completely under direct vision with the help of hysteroscope.
7. Hysteroscopic Septal Resection
A septum in the uterus can cause repeated miscarriages and inability to conceive. Hysteroscopic removal of a uterine septum is generally the preferred method as the intervention is relatively minor and safe.
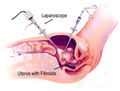
8. Laproscopic Myomectomy
Uterine fibroids are the most common benign tumors occurring in women in the reproductive age group. Fibroids are present in approximately 5-10% of the patients presenting with infertility. Laparoscopic myomectomy (removal of fibroid) can be considered as a safe technique with an extremely low failure rate and good results in terms of pregnancy outcome.
9. Laparoscopic Adhesiolysis
Pelvic adhesions are bands of scar tissue that grow between pelvic structures binding them together. Adhesions can result from diseases (Endomertriosis, PID, tuberculosis), prior surgeries or radiation. Laparoscopic adhesiolysis is a minimally invasive procedure that removes adhesions and restores reproductive health with a return of fertility.
10. Laparoscopic Ovarian Drilling
Laparoscopic ovarian drilling is a surgical treatment that can trigger ovulation in women who have polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). Electrocautery or a laser is used in the procedure to make punctures in the ovaries. It is done under general anaesthesia.




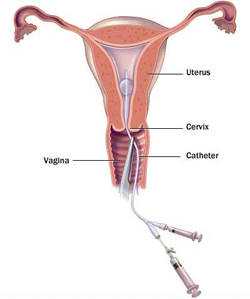
 Sonosalpingography(SSG) is a diagnostic procedure used for the evaluation of
the uterine cavity and patency of fallopian tubes. It aids in the diagnosis of sub mucous fibroid polyp and intrauterine lesions. Under ultrasound guidance, a slow and deliberate injection of 200ml of physiologic saline into the uterine cavity is accomplished via a catheter. By visualising the flow of saline the uterus and tubes can be studied.
Sonosalpingography(SSG) is a diagnostic procedure used for the evaluation of
the uterine cavity and patency of fallopian tubes. It aids in the diagnosis of sub mucous fibroid polyp and intrauterine lesions. Under ultrasound guidance, a slow and deliberate injection of 200ml of physiologic saline into the uterine cavity is accomplished via a catheter. By visualising the flow of saline the uterus and tubes can be studied.